Standardized and automated data processing.
Muscle-BIDS
Why Muscle-BIDS
For automated data processing of processing with various tool-boxes data management is important. For this, the muscle MRI community is developing the Muscle BIDS data structure. When data is organized in this way all needed parameters and data sets can automatically be found, which enables automated processing and evaluation of large data sets. Furthermore, each toolbox that is Muscle-BIDS compatible can run its analysis on the same data without the need to restructure the data input. The last advantage is that the output is also standardized which makes the comparison of results and methods more convenient. More about Muscle-Bids can be found here».
All data generated within the muscle-atlas projects will be stored in the Muscle-BIDS format. The main processing tool we use (QMRITools) for our standardized qMRI muscle studies uses dedicated Muscle-BIDS compliant scripts that do not need any user interaction. Muscle-BIDS pipelines developed for the Muscle-Atlas project supports the following steps:
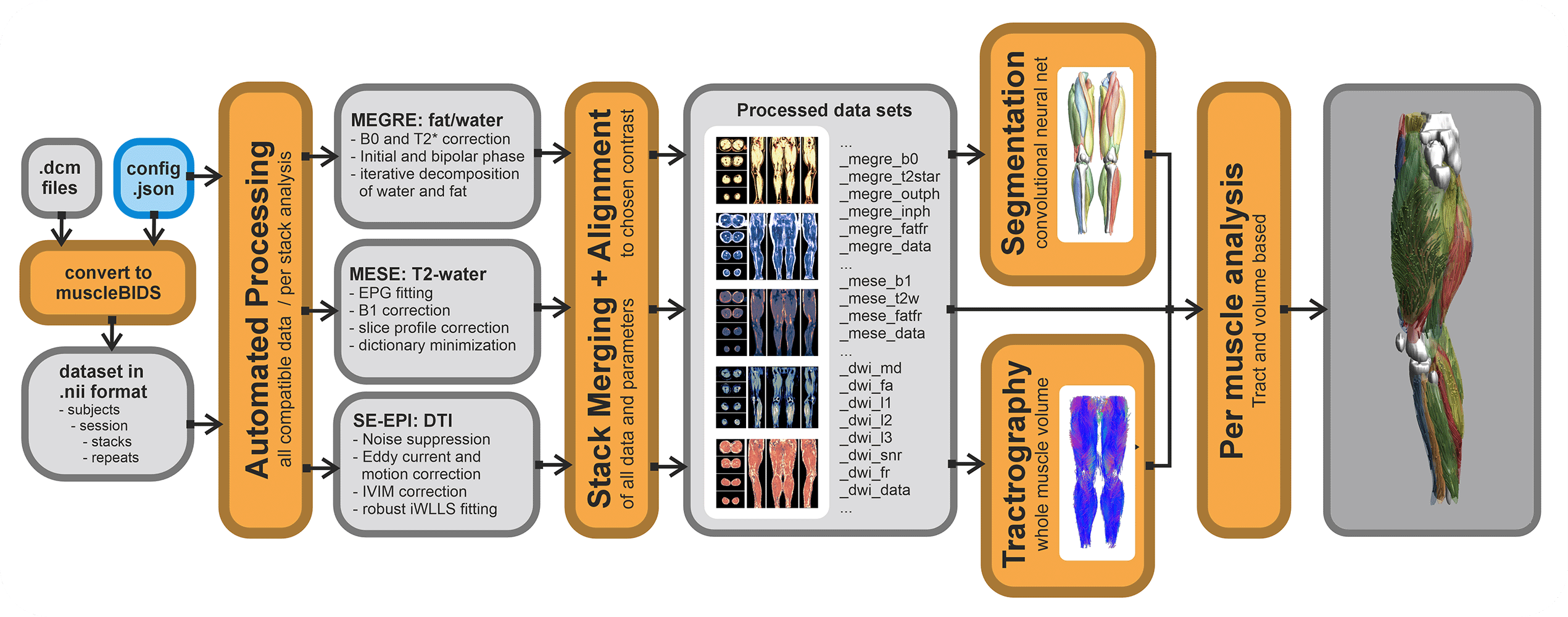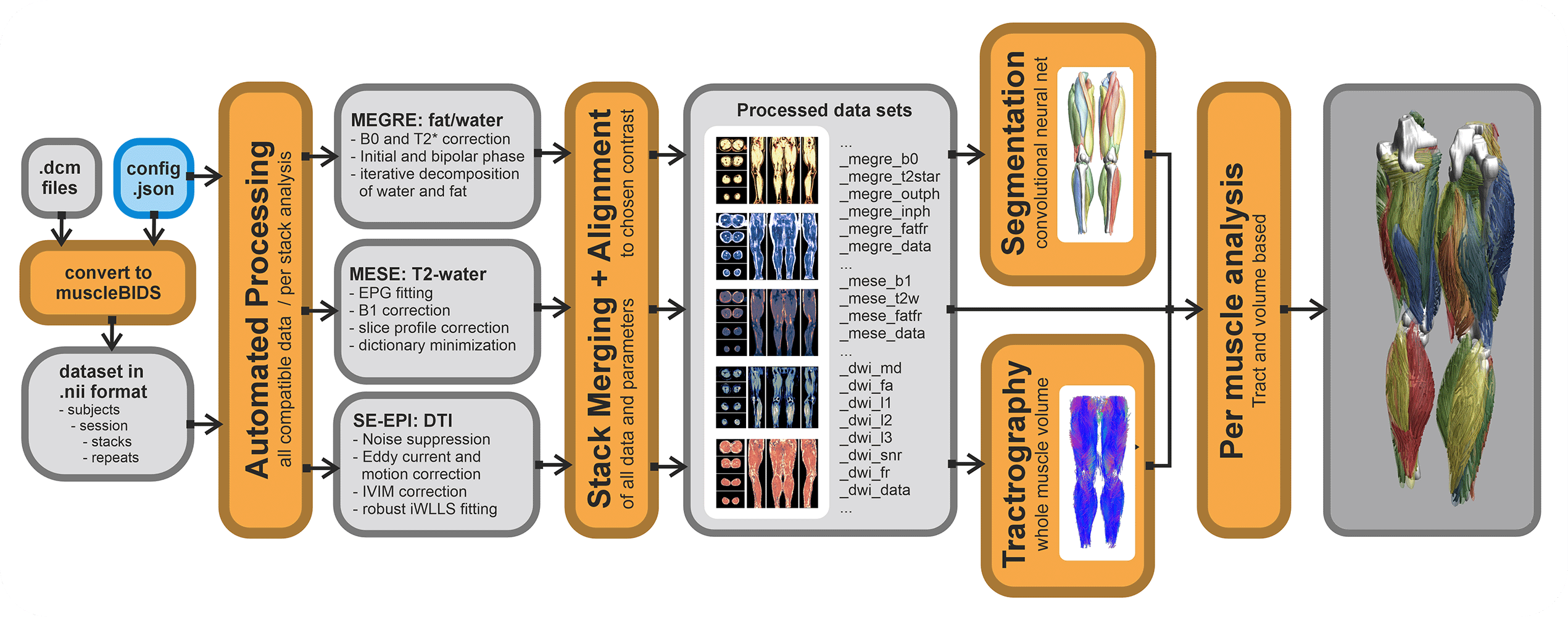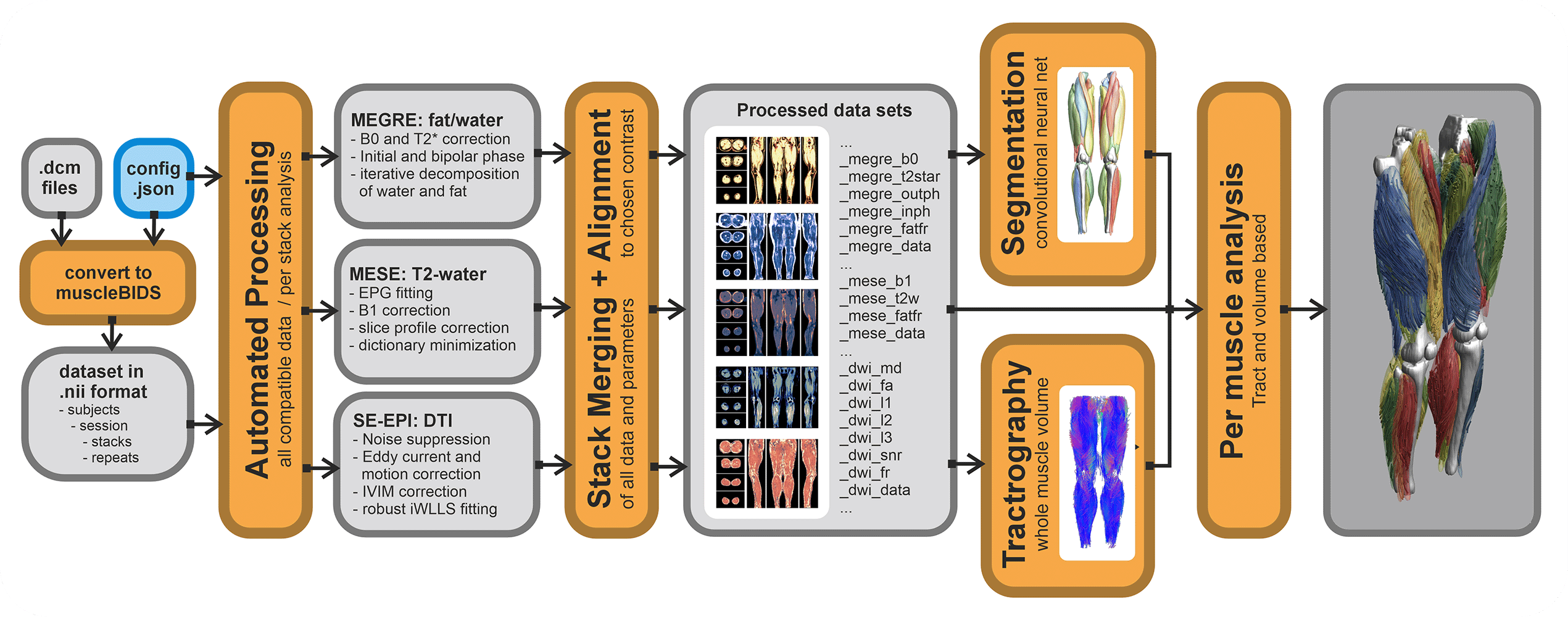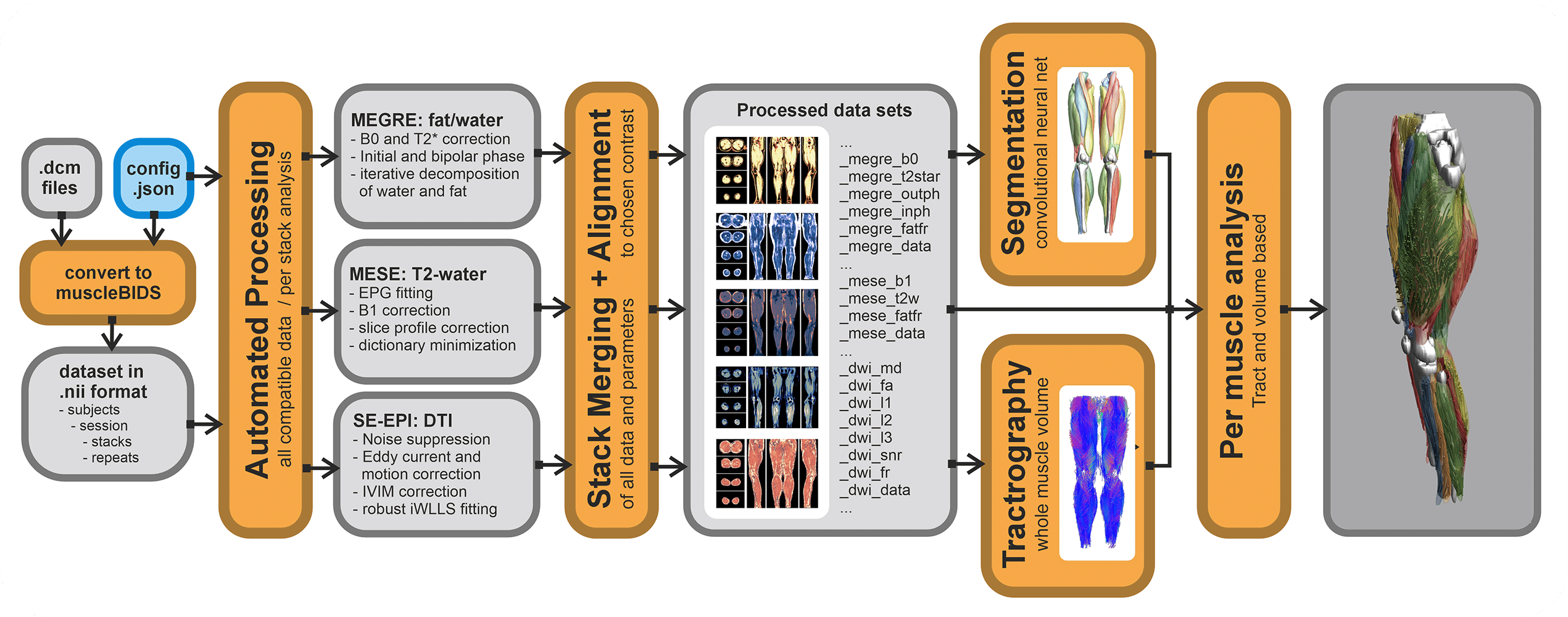
- Conversion of DICOM to raw Muscle-BIDS NIfTI
- Processing of Muscle-BIDS data
- DTI, IVIM, T2-mapping and Dixon
- Data merging
- Analysis of processed Muscle-BIDS data
- ROI analysis
- Tract based analysis
Data structure
To prevent ambiguity most MRI acquisitions are stored in predefined folders. Muscle-BIDS-compliant software will look in these folders for their needed raw source data. The following folders have been defined in Muscle-BIDS. QMRITools uses the following subfolders to store data in the Muscle-BIDS dataset. More about data structures can be found here». Within a data structure standardized entities and suffixes are used to identify which files contain what, more information about file naming can be found here».
anat: Structural imaging for anatomical or diagnostic reference (e.g T1 or T2).dwi: Diffusion-weighted data (e.g. DTI or IVIM).dix: Dixon data.quant: Relaxometry data (e.g. T1 or T2 mapping).seg: Segmentation labels (e.g. manual segmentations).raw: Unspecified non-BIDS files.
An example of a folder structure is shown below:
├─sub-cont001/
│ ├─ses-visit1a/
│ │ ├─dix/
│ │ ├─quant/
│ │ └─raw/
│ ├─ses-visit1b/
│ │ ├─dix/
│ │ ├─dwi/
│ │ ├─quant/
│ │ └─raw/
│ └─ses-visit2/
│ ├─dwi/
│ └─raw/
├─sub-pat0054/
│ ├─ses-visit1/
│ │ ├─dwi/
│ │ ├─quant/
│ │ └─raw/
│ └─ses-visit2/
│ ├─dix/
│ ├─dwi/
│ └─raw/
└─sub-test002/
├─ses-visit1/
│ ├─quant/
│ └─raw/
└─ses-visit2/
├─dwi/
├─quant/
└─raw/